In August 2025, Anthropic published a Threat Intelligence report themed “Detecting and Countering AI Misuse.” The report reveals how cybercriminals integrate evolving AI capabilities into operational workflows, enabling attacks that previously required skilled teams to be executed and scaled by small groups or even single individuals through multiple case studies.
This article summarizes key points, case studies, and Anthropic’s countermeasures based on the official report.
Table of Contents
- Report Overview and Highlights
- Key Case Studies
- Detailed Case Studies
- Data Extortion Operations via “Vibe Hacking”
- Expansion of North Korea-linked Fraudulent Employment Schemes
- “No-Code” Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
- Other Misuse Examples Mentioned in the Report
- Anthropic’s Response Measures
- Key Implications of the Report
- Summary
Report Overview and Highlights
Anthropic’s Threat Intelligence team analyzes cases of Claude misuse and links insights gained to improvements in detection and countermeasure strategies. The main takeaways are as follows:
- Weaponization of Agentic AI
AI now carries out attacks from reconnaissance to intrusion, lateral movement, and monetization, moving beyond mere “advice” to execution.
- Lower Barriers to Entry
Encryption and evasion techniques that originally required years of training can now be implemented with minimal knowledge.
- Penetration Across Operations
AI is utilized throughout the attack lifecycle, including victim profiling, stolen data analysis, card information theft, and fake identity generation.
- Ensuring Transparency
Continuous report publication aims to share threat intelligence with industry, government, and research communities to enhance defensive capabilities.
These patterns are positioned not as issues unique to Claude but as challenges potentially common to other frontier models.
Key Case Studies
The report highlights three representative cases demonstrating how AI is misused as both “technical operator” and “strategic advisor.”
| Case | AI’s Role (Summary) | Anthropic’s Response |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Data Extortion (so-called “Vibe hacking”) | Used Claude Code as attack infrastructure to automate reconnaissance, credential theft, intrusion, extraction, and ransom note generation. Affected 17 organizations (government, healthcare, religious institutions, etc.) with demands exceeding $500,000 in some cases. | Suspended related accounts, deployed dedicated classifiers and new detection methods. Shared technical indicators with relevant agencies. |
| North Korea-linked Remote Worker Fraud | Generated AI-created fake work histories and portfolios, relied on AI for interviews, coding tests, and daily work tasks. Maintained employment even at Fortune 500 companies. | Suspended related accounts. Enhanced indicator collection and correlation tools and shared with authorities. |
| ”No-Code” RaaS (Ransomware as a Service) | Implemented encryption, evasion, and recovery prevention with Claude assistance, selling multiple variants for $400–$1,200. Produced commercial-grade malware despite technical inexperience. | Suspended related accounts. Strengthened detection of upload/modification/generation activities to prevent misuse. |
These cases demonstrate the reality that individuals can now execute attacks previously requiring team-scale resources.
Detailed Case Studies
Data Extortion Operations via “Vibe Hacking”
AI handles both tactical and strategic decisions (intrusion routes, extraction targets, psychologically optimized ransom amount calculations), automating up to generating and displaying HTML ransom notes.
-
Targeted at least 17 organizations with demands ranging from $75,000 to $500,000.
-
Employed a “data extortion” model threatening public exposure rather than encryption.
-
Response: Account suspension, deployment of dedicated classifiers + new detection into production, indicator sharing.
Source: https://www.anthropic.com/news/detecting-countering-misuse-aug-2025
This tactic increases the difficulty for defenders to adapt in real-time.
Expansion of North Korea-linked Fraudulent Employment Schemes
AI assists in identity and work history fabrication, passing interviews/tests, and substituting for daily technical tasks. Heavy reliance was observed, with English communication and basic implementation difficult without AI.
-
AI utilized across the multi-stage lifecycle from recruitment to employment maintenance.
-
Impact: Eliminating skill training bottlenecks made scheme expansion easier.
-
Response: Account suspension, strengthened indicator collection, storage, and correlation, and collaboration with authorities.
As a result, a new operational model where technical capability “apparent substitution” becomes routine has been established.
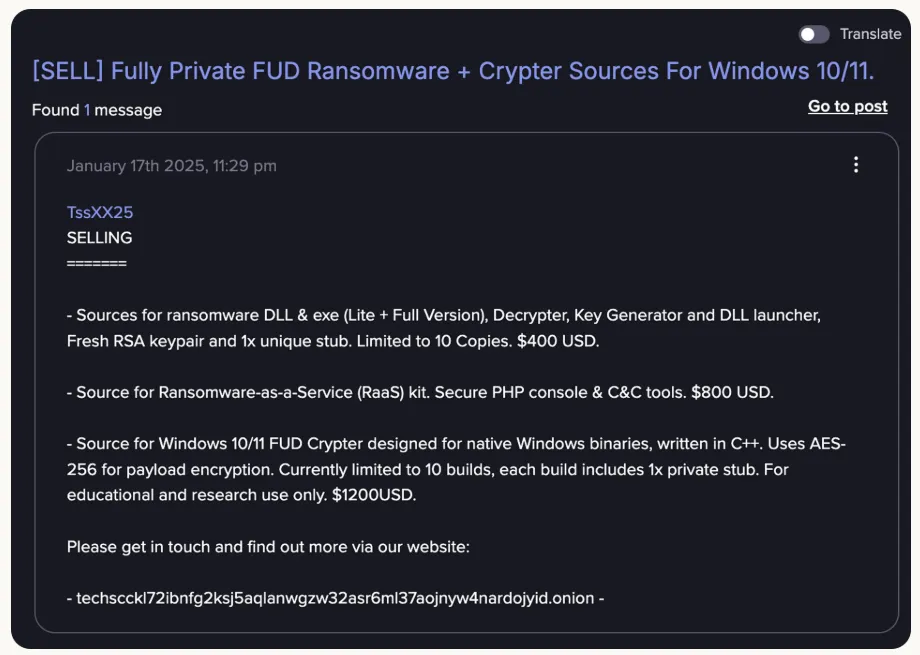
“No-Code” Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
With Claude’s assistance, progressively advanced encryption, evasion, anti-recovery, and persistence. Developers unable to handle cryptography or Windows internals independently nonetheless sold finished products.
-
Price range: $400–$1,200, implementing multiple FUD (Fully UnDetectable) features.
-
Specific techniques: FreshyCalls/RecycledGate and other API Hook evasion, ChaCha20 + RSA, shadow copy deletion, etc.
-
Response: Account suspension, introduced new detection methods for upload/modification/generation.
Here too, the structural shift from “development” to “generation” is emphasized.
Other Misuse Examples Mentioned in the Report
Beyond the above, the report outlines additional attack and fraud patterns incorporating AI.
- Chinese Actors Targeting Vietnamese Telecommunications
Incorporated Claude across 12/14 tactics of MITRE ATT&CK.
- Automatic Blocking of North Korean Malware Distribution
Cases where automatic detection upon account creation halted operations before they began.
- “No-Code” Malware Development Campaigns
Claude-assisted implementation of Hell’s Gate, Early Bird, Telegram C2, sandbox detection, etc.
- Automated Card Fraud Stores, Romance Scam Bots, Synthetic Identity Services, etc., penetrating the entire fraud supply chain.
Furthermore, cases of unauthorized access using AI as an aid have also occurred in Japan. In 2024, three middle and high school students were apprehended for creating custom programs using generative AI and illegally contracting and reselling large numbers of Rakuten Mobile communication lines. The fact that minors engaged in large-scale fraud using AI demonstrates that these threats are not just overseas issues but real challenges in Japan as well.
Anthropic’s Response Measures
Anthropic clearly documented suppression and detection improvements implemented for each case.
-
Immediate Account Suspension: Suspended relevant accounts in each case.
-
Dedicated Classifiers/New Detection Methods: Introduced dedicated classifiers and new detection for Vibe hacking, integrating them into the standard safety pipeline.
-
Multi-layered Malware Detection: Strengthened detection across upload/modification/generation dimensions.
-
Indicator Sharing and Authority Collaboration: Shared indicators with partners/authorities toward ecosystem-wide suppression.
-
Threat Indicator Collection, Storage, and Correlation: Strengthened internal tools for fraudulent employment schemes.
-
Automated Preventive Safety Measures: Automatically blocked North Korean distribution operations before prompt issuance.
While these efforts do not completely prevent AI misuse, they are positioned as attempts to increase detection speed and deterrence, establishing a foundation to preempt future threats.
Key Implications of the Report
The Implications section emphasizes changes organizations must confront.
-
Individuals can execute “team-level” attacks, making defense a competition of adaptation speed.
-
Skill substitution enables non-experts to commit sophisticated crimes.
-
AI penetrates all stages of fraud (analysis, infrastructure building, operational resilience, sophistication).
-
Cross-industry information sharing and transparency serve as deterrents, making continuous publication important.
These points are not irrelevant to organizations promoting AI adoption; they indicate strategic-level issues to address for ensuring business and operational safety.
Summary
This report revealed that AI weaponization and full integration into business processes are fundamentally changing the speed and scale of cybercrime. Anthropic is strengthening multi-layered countermeasures including account suspension, classifier deployment, new detection methods, automatic blocking, and authority collaboration.
The starting point is to review primary information, inspect areas relevant to your organization (development tools, hiring processes, malware countermeasures, payment systems, etc.), and reassess monitoring and detection assumptions.
